Translation has long ceased to be painstaking work with a dictionary. Modern translation specialists have many tools that make translation much faster and more convenient. For example, memory translation allows translators to save successful translations for future use, instead of translating content again every time.
How do your translation contractors work? What tools can simplify your work with texts in a foreign language? If you want to find out the answers, this article is for you.
Translation memory is a database that contains small pieces of texts: for example, phrases or sentences. They’re compiled according to the rules of a particular language and can be freely used for translation purposes. TM allows translators to save a significant amount of time on translation, while maintaining the quality and improving consistency of texts.
The translation memory systems have been developing since the 1950s. At first, they allowed the translation of limited vocabulary ranges. Then, it became much more efficient thanks to the development of personal computers and computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools. Now machine translation and artificial intelligence are making translations even better.
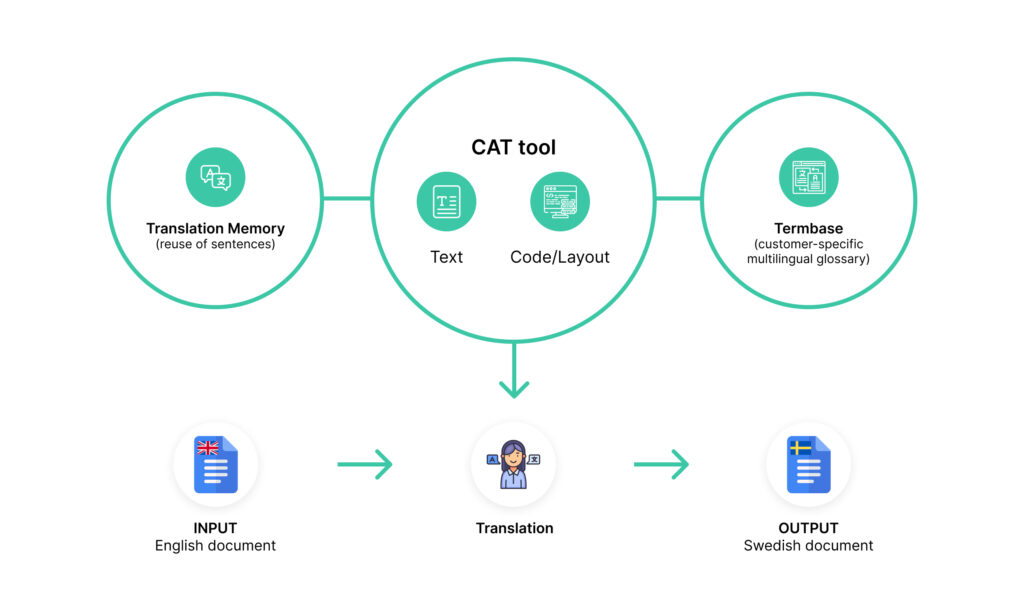
Translation memory is the ability to use a previous translation of a text segment so that you don’t have to translate phrases again every time. Once translated, words and sentences remain in the computer’s memory and can be retrieved. To do this, most modern specialists use CAT tools in their work. Thus, they don’t translate the same words from the source language every time: they already have a prepared base of translation units made by them and other professionals.
CAT tools are applications that automate the translation process and make translations more accurate. To use it, a specialist loads a source text into the program, divides it into fragments, and then translates each fragment. Correctly translated phrases will remain in the program, and the linguistic database becomes larger with new translations. In future projects, it allows the specialist to just compile a translation using previous projects with minor modifications.
Here are the result of a survey among more than 3000 translators worldwide (note: most translators use more than one tool regularly):
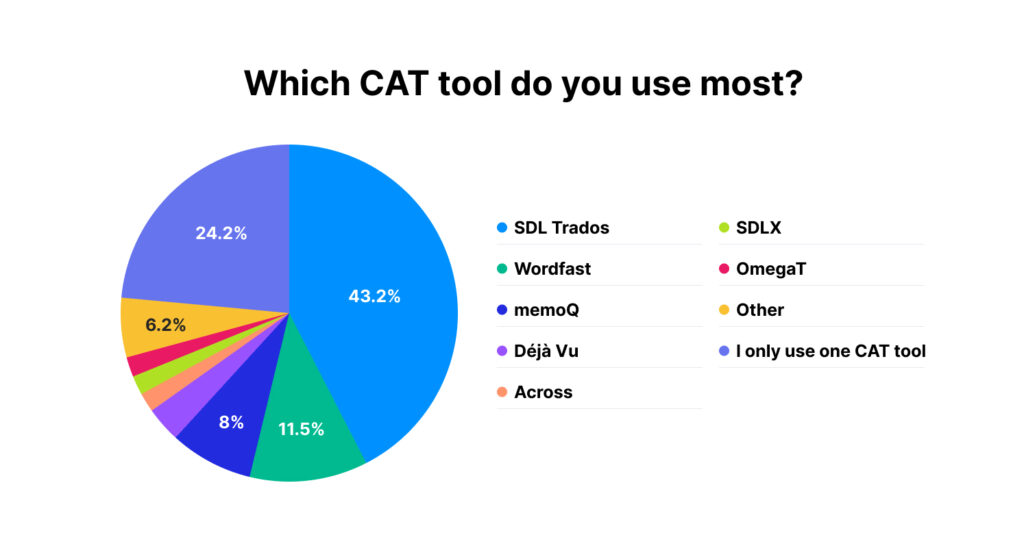
At first glance, it may seem that TM is a perfect system for translations. You don’t even need to do anything: upload a source file, edit the phrases, and the translation is ready. However, like any computer system, existing TM systems have pros and cons.
Some people still confuse translation memory with glossaries and machine translation. Here’s why it’s worth distinguishing between them:
Translation memory systems differ depending on the tasks of translators. As a rule, they are divided into two types:
Depending on the provided language services, the systems can be free (OmegaT, SmartCat, BasicCAT) and paid (Trados, Memoq, Memsource). They include a variety of options for translators, from import and export to automatic translation and even networking.
Not all areas can benefit from the use of translation memory: for example, literary translation or marketing texts often need more creativity. However, for many areas, translation memory will be extremely useful since it maintains consistency, speed, and quality of translation.
Technical translation requires using specific terminology and standard “dry” wording. TM systems will track the correct use of technical terms and make the text consistent.
In the video game localization process, the texts should not be standardized, but all the names of weapons, races, or special devices should always remain the same. In addition, TM will help create more vivid images of characters using particular language features. This will make the gaming experience more involving and exciting.
Just like in technical texts, it’s necessary to follow the rules and use the key terminology. In translating legal documents, the price of an error can be high, so you can’t do without the use of special software programs.
Using manuals will help users quickly figure out how to use your product. Therefore, every detail must be named correctly, and the translation must be “native” enough for people to understand the instructions correctly.
Some errors in the translation of foreign software don’t cause trust, and users immediately perceive the product as low quality. Moreover, these errors can lead to problems using the software. It’s essential to monitor the literacy of the translation and use best practices that have already been successfully implemented in other products.
When looking for a professional translation, you shouldn’t work with the company with the lowest prices, although it may be the best one. As you can see, it’s also important to take into account not only the experience of the company and the cost of work, but even the software used. For example, translation memory systems will help translate texts better, while speeding up the work and saving your money.
We at Palex, localization services provider, use special CAT tools to apply all the experience that we’ve had over 20 years of work in the localization services industry. We work with multiple languages according to the industry standards. For each language pair, we strive to find the most successful translation options for any text, whether it be a medical, educational, or commercial one. Drop us a line at [email protected]. We’ll be glad to work on your localization project.


